Parole étudiante
Ils l’ont vécu et ils en parlent.
Parole enseignante
Transmission des savoirs, accompagnement des étudiant(e)s
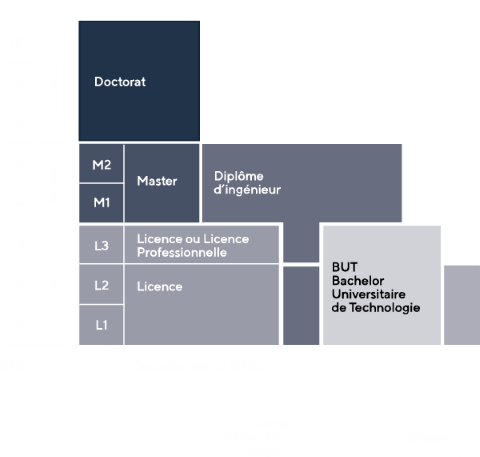
Schéma des études
Une université professionnalisante : la 1ère université française en apprentissage
Avec 25% d’étudiants en apprentissage, nous sommes une passerelle entre le monde universitaire et de celui de l’entreprise
Une université qui vous insère rapidement sur le marché du travail
En lien permanent avec le monde socio-économique, nous travaillons dans une optique d’insertion rapide de nos étudiants sur le marché du travail. Le temps d’accès au 1er emploi après un master de notre université est de 4,4 mois.
Une université de proximité qui vous conseille et vous oriente au quotidien
Dotés d’une équipe de conseillers et d’experts dans le domaine de l’orientation et de l’insertion professionnelle, nous vous informons et vous accompagnons tout au long de votre cursus.
Une université engagée sur la thématique des villes durables
Nous représentons un quart de la recherche nationale sur le sujet et contribuons à créer un avenir sociétal et environnemental meilleur.


